The Vitrification Process of Embryos and Oocytes in Assisted Reproductive Technology
Vitrification of embryos or oocytes is the best procedure for women who want to focus on their careers and plan future families in their 40s. Also, this procedure will be effective for women undergoing cancer treatment or who are experiencing certain disorders or undergoing fertility treatments.
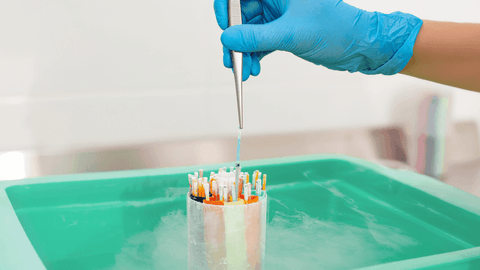
What Is the Vitrification Method?
A process called vitrification is a fantastic breakthrough for preserving oocytes (egg) and embryos, and this process has transformed today's ART industry. It is an advanced technique that leads to a glass-like formation. The freezing method happens so rapidly that the water molecules don't get the time to form ice crystals but instead immediately solidify into a glass-like structure, thus avoiding freezing injuries to the human oocytes and embryos.
The Process of Vitrification Method
The process of vitrification consists of the following steps:
- The eggs or embryos are exposed to a high concentration of cryoprotectants, which allows rapid
- dehydration of the reproductive cells
- Eggs or embryos are put into tiny storage devices that will facilitate ultra-rapid cooling.
- The storage devices containing the eggs/embryos are cooled at 1000 degrees per minute.
- The high cooling rate and the use of the high concentrations of the cryoprotectants allow the contents of the storage device that is oocyte/embryo and fluid to turn into a glass-like substance instead of ice.
- Then, they are stored in a nitrogen-filled tank that is kept at -196 Celsius.
- When needed, the oocyte or embryos are warmly incubated. The preservative is washed away
- After 3-4 hours, the eggs can be injected with a single sperm, and the embryos can be transferred to the uterus within 24 hours.
Vitrification of Embryos
It is done to preserve the excess embryos. In IVF, the practice is to transfer a smaller number of fresh embryos into the uterus. If the first cycle fails, then a frozen embryo transfer can be done without undergoing the hassles of ovarian stimulation again, followed by egg retrieval.
Vitrification plays a significant role in the medium to severe cases of ovarian hyperstimulation. In approximately 5-10% of cases, the body overreacts to hormonal stimulation during extracorporeal fertilization (occurring outside the body).
Due to medical reasons, it is not advisable to transfer fresh embryos. Therefore, all embryos are frozen and moved after hyperstimulation has entirely subsided. In cases of polyps and hydrosalpinx, a doctor recommends frozen embryo transfer.
Vitrification of Human Oocytes
The vitrification procedure is more complicated than slow freezing, but this technique preserves and keeps the eggs completely fresh even after a few years. It has also been seen that the pregnancy success rate from this technique can be compared to new IVF cycles.
The problem with freezing eggs, relative to sperm or embryos, is that eggs are mostly made of water. Ice crystals would form when freezing was attempted, and these crystals would damage the cell's structure, making them unusable. The key to the whole process is a smooth transfer of fluids from the egg to another medium, while it is made
sure that anti-freeze is slowly flowing in at the same time. Once this step is carefully done, the eggs quickly freeze or vitrify. The quick cooling allows the eggs to survive without any ice crystals forming - these could have damaged the delicate cellular parts, which could have been devastating. Nowadays, vitrification of oocytes has become a standard part of infertility treatment.
What Are the Advantages of The Vitrification Process?
The main advantages of vitrification over slow freezing are discussed below:
- Ice crystals do not damage vitrified oocytes or embryos.
- The live birth rate of vitrified embryos is higher than the of slow-frozen embryos. Because in slow freezing, approximately 20-30% of embryos do not survive after the thawing process.
- It also eliminates the need for the freezing unit in the process of slow freezing.

