PCOS - Symptoms, Causes and Diagnosis
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal disturbances on a global basis and affects women worldwide. According to statistics from WHO, the condition affects approximately 8-13% of women of reproductive age, with a 70% share of undiagnosed cases.
The ovaries play an essential role in conception and are necessary components of the female reproductive system. In addition to being responsible for the production of oocytes and oestrogen, they also regulate the development of key female secondary characteristics. Suffering from PCOS thus has a significant impact on a woman's reproductive health, and early recognition and treatment of the condition is vital.
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal condition caused by an excess of male hormones and a deficiency of female hormones. The disturbance of the hormonal balance leads to irregular or absent ovulation, which in turn impacts a woman's ability to conceive.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
The ovaries are one of the female reproductive system's major components. They're located in the lower abdomen on both sides of the uterus, and they produce eggs and sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
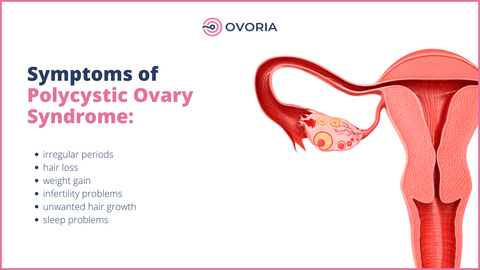
Symptoms of PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can result in a wide variety of symptoms. The severity of these symptoms can vary among individuals. However, it should be noted that not everyone with PCOS will experience all of these symptoms. Common signs and symptoms of PCOS may include:
- Irregular periods: some women can experience irregular periods, while others suffer from heavy menstrual bleeding. Both of these issues are related to PCOS.
- Hair loss: Women of reproductive age with polycystic ovarian syndrome could experience thinning hair, which could worsen with increasing age.
- Excessive hair growth or hirsutism: Certain areas of the body such as the face, arms, back, chest, thumbs, and toes may grow excess hair. This excess hair is related to hormonal imbalance due to increased androgen production that occurs for women with PCOS.
- Acne or oily skin: The male hormone testosterone can make the skin oilier than usual and cause breakouts on the face, chest, and upper back.
- Weight gain: many women with PCOS, gain weight and struggle with obesity that is difficult to manage.
- Infertility: Although PCOS is one of the leading causes of female infertility, not every woman who has PCOS will experience the same fertility problems. Some women with PCOS can get pregnant without assistance.
- Sleep problems: If a woman has PCOS, she can notice that she has trouble sleeping. She may experience a sleep disorder called sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is when a person stops breathing for short periods during sleep.
- Darkening of skin: women's skin may become very dark in certain areas, such as their armpits and neck. This is called acanthosis nigricans.
If you suspect you have PCOS or are experiencing symptoms, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and management plan.
What Causes PCOS?
While the exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Research indicates that the manifestation of the condition may be caused by;
- Genetics: a family history of PCOS may increase the chances of you developing the condition. Although specific genes associated with PCOS have not yet been identified, there is a general correlation with genetics. It thus appears to be a genetic component to the disorder.
- Insulin resistance: women diagnosed with PCOS often have insulin resistance, meaning that the body's cells don't respond as intended to insulin. As a result, an overproduction of insulin and general higher levels of insulin in the blood can potentially contribute to symptoms associated with PCOS. It is important to note that the insulin resistance, if persistent over time, can lead to type 2 diabetes.
- Hormonal imbalance: as previously mentioned, the hormonal imbalance caused by an excess production of androgens (male hormones) is likely associated with PCOS.
- Inflammation: women suffering from low-grade inflammation might be more prone to develop PCOS. Inflammation is the immune system's response to harmful stimulants, and is considered a part of the body's defence mechanism.
- Lifestyle factors: obesity is often associated with PCOS, meaning that weight management and generally maintaining a healthy lifestyle help manage the disorder.
- Foetal development: researchers suggest that being exposed to certain factors (e.g. insulin resistance in the mother, androgen exposure) during foetal development may enhance the likelihood for developing PCOS.
Be aware that PCOS is a complex condition, and the interrelation of the mentioned factors can vary from person to person. Moreover, while extant research suggests that these factors are associated with PCOS, their prevalence can not guarantee that an individual will develop the condition. It is however important that you consult with your healthcare provider if you suspect that you have PCOS or are experiencing symptoms.
Can PCOS Affect Your Fertility?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is typically associated with hormone imbalances. The hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle are out of balance, making conception impossible for a woman with PCOS. If women with PCOS have immature eggs in their ovaries, they are referred to as PCOS patients. IVF treatment is the most successful fertility treatment for PCOS patients because it helps stimulate egg maturation.
Diagnosis - How is PCOS Diagnosed?
Doctors run a physical examination to check for acne and excess hair growth, as well as to examine the thickness of your hair. Your healthcare provider should be made aware if you've experienced hair loss or thinning. Moreover, a pelvic ultrasound may be performed to check for an increased number of small follicles (cysts). The doctor may also ask you to provide a number of different blood tests that check various factors related to your PCOS. Some of the tests include:
- Thyroid function test: used to examine the functioning of the thyroid gland, which plays an important role in regulating metabolism. The test is relevant since thyroid dysfunctions and PCOS often coexist.
- Lipid level test: used to measure cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Women with PCOS can be at an increased risk of developing cardiovascular issues.
- Fasting glucose test: used to measure blood glucose levels, and assesses the body's ability to regulate glucose. As PCOS is associated with high levels of glucose, fasting glucose tests can assist in the evaluation of the body's insulin sensitivity.
Through the conduction of several different tests, doctors can come to some conclusions regarding problems with the patient's fertility and cysts in the ovaries.
PCOS Treatment Options
As with other treatments, the effectiveness of PCOS treatment depends on managing various factors, including the individual's diet and exercise level. Some women may need to take medicine or make subtle changes to the way she eats. Some of the recommendations for PCOS treatment are:
- PCOS diet: to properly manage PCOS symptoms, a healthy diet is essential, especially if you consider the association between the disorder and insulin resistance. Therefore, focusing on the maintenance of a balanced diet including carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Exercise for PCOS: as women with PCOS often struggle with regulating their weight, regular physical activity is crucial. Other benefits include the improvement of insulin sensitivity, and the overall well-being.
- Birth control pills for PCOS: birth control pills are often prescribed to women with PCOS as they help regulate menstrual cycles, manage androgen-related symptoms, while also providing endometrial protection.
- PCOS Medicine: there are various medications that are prescribed to individuals suffering from PCOS to manage specific symptoms related to the disease (e.g. metformin, anti-androgens, ovulation-inducing medications).
- PCOS Surgery: in some special cases, surgical interventions may be recommended. The available surgeries include ovarian drilling (to improve ovulation) or laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy (removal of cysts).
Note that the disorder is considered a chronic condition, and that there is no available cure for PCOS. However, the treatment options discussed are proven to effectively manage symptoms, meaning that living with PCOS is possible.
Living with PCOS - How to Manage Health Problems
Living with PCOS involves adopting a balanced diet and prioritising regular physical activity to regulate blood sugar and losing weight. Medications can assist in addressing specific symptoms. While PCOS is chronic and not curable, the treatment options above ensure effective symptom management, allowing individuals affected by the condition to live fulfilling lives. Close collaboration with healthcare professionals is essential, as they can offer tailored approaches to address personal health needs and goals.
References
- Kahsar-Miller, M. D., Nixon, C., Boots, L. R., Go, R. C., & Azziz, R. (2001). Prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in first-degree relatives of patients with PCOS. Fertility and sterility, 75(1), 53-58. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0015028200016629
- Dewailly, D., Hieronimus, S., Mirakian, P., & Hugues, J. N. (2010, February). Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). In Annales D'endocrinologie (Vol. 71, No. 1, pp. 8-13). Elsevier Masson. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0003426609003126
- De Leo, V., Musacchio, M. C., Cappelli, V., Massaro, M. G., Morgante, G., & Petraglia, F. J. R. B. (2016). Genetic, hormonal and metabolic aspects of PCOS: an update. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 14(1), 1-17. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12958-016-0173-x?fbclid=IwAR3u7n94mGc2pK_e5lUwzobgtqEM7XEZvDbVFTS7wDQzqjdoOWDiyFhQsi8

